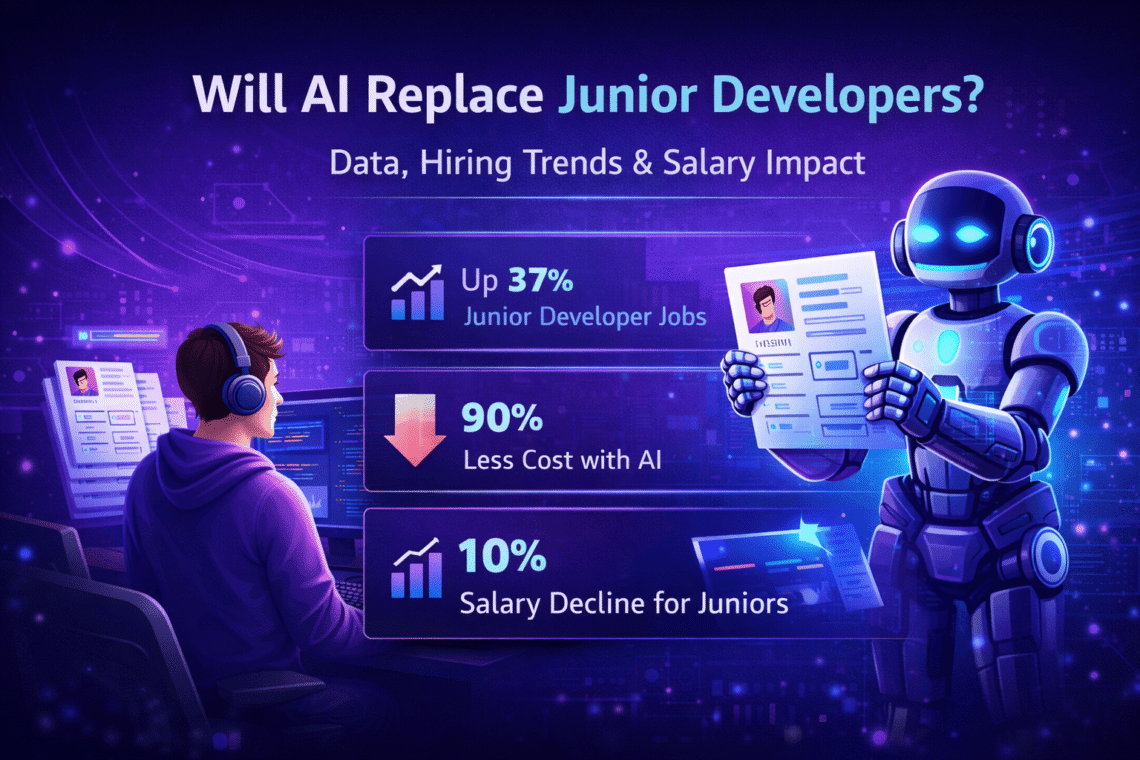
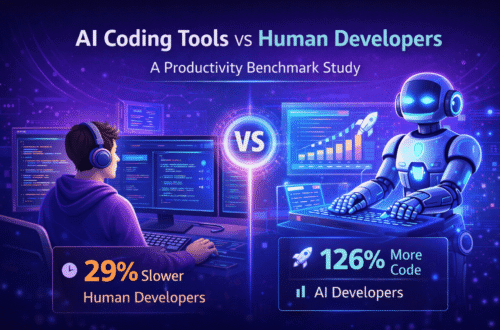
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence tools in software development has intensified concerns among students, bootcamp graduates, and early career engineers. Coding assistants, automated testing systems, and productivity platforms are now integrated into many development workflows. As these tools become more capable, a central question has emerged: will AI replace junior developers?
Junior developers traditionally perform structured implementation tasks under supervision. These responsibilities often include writing basic features, fixing smaller bugs, assisting with testing, maintaining documentation, and supporting senior engineers during larger projects. Because some of these tasks can now be partially automated, there is growing speculation about the long term stability of entry level roles.
At the same time, hiring patterns in the technology sector have experienced fluctuations due to broader economic adjustments. Workforce restructuring, funding shifts, and global competition have influenced entry level opportunities. It is important to separate economic cycles from technological change when evaluating job market trends.
This report examines available hiring trends, role evolution, and salary movement to assess whether junior developer positions are being eliminated or redefined. Rather than relying on speculation, the analysis focuses on how responsibilities, expectations, and compensation structures are adapting in 2026.
Which Junior Roles Are Most at Risk of Disruption
While junior developer positions are not disappearing entirely, certain types of entry level roles face greater adjustment due to automation, standardization, and increased competition. Risk is typically associated with task simplicity rather than job title.
Basic Template Customization Roles
Positions focused primarily on modifying existing templates, adjusting user interface components, or implementing minor layout changes may face higher competition. When tasks follow predictable patterns, productivity tools can complete them more efficiently.
Developers in these roles may need to expand their technical scope to maintain strong growth potential.
Repetitive Script Maintenance
Jobs centered on writing simple scripts with minimal system interaction may become more streamlined through automation. If responsibilities do not include debugging, integration, or optimization, differentiation becomes limited.
Increasing involvement in broader system workflows strengthens long term stability.
Low Complexity Bug Fixing Only Positions
Roles that focus solely on minor bug resolution without exposure to architecture or deployment processes may offer limited advancement. As automated testing and monitoring tools improve, some repetitive debugging tasks require less manual effort.
However, complex debugging, root cause analysis, and production incident management still require human reasoning.
Which Junior Roles Are Growing in 2026
While some narrow task based positions face adjustment, several entry level roles continue to expand as software systems become more complex and infrastructure heavy. Growth areas typically involve exposure to modern development environments and cross functional collaboration.
Cloud Support and Infrastructure Assistants
Organizations migrating to cloud platforms require engineers who understand deployment basics, environment configuration, monitoring tools, and infrastructure documentation. Junior roles supporting cloud operations remain relevant as companies expand digital services.
Foundational knowledge of virtual machines, containers, networking basics, and deployment workflows improves employability in these positions.
DevOps and Continuous Integration Support
As development teams emphasize automated testing and deployment pipelines, junior engineers who can manage build processes, assist with integration scripts, and monitor deployment systems are valuable contributors.
Exposure to version control workflows, automated testing environments, and release management practices strengthens entry level profiles.
Data Engineering Support Roles
Companies increasingly rely on structured data pipelines. Junior developers who assist in data cleaning, transformation workflows, and database maintenance gain practical experience in data driven environments.
Understanding SQL fundamentals, data validation, and pipeline documentation supports growth in this area.
Security and Compliance Support
Security practices continue to evolve. Entry level developers who assist in vulnerability tracking, basic secure coding practices, and compliance documentation contribute to organizational risk management.
Even foundational knowledge of authentication systems and access control principles enhances relevance.
Why Junior Roles Still Matter in Software Development
Despite evolving workflows and automation tools, junior developer roles remain an essential part of software engineering teams. Entry level hiring supports long term workforce sustainability, knowledge transfer, and team scalability.
Talent Pipeline Development
Organizations rely on structured career progression. Junior developers grow into mid level and senior roles over time. Without consistent entry level hiring, companies risk future skill shortages and leadership gaps.
Training new engineers ensures continuity in technical knowledge and organizational standards.
Workload Distribution
Large projects involve a wide range of tasks, from feature implementation to documentation and testing support. Junior developers help distribute workload across teams, allowing senior engineers to focus on architecture, optimization, and strategic decisions.
Balanced team composition improves efficiency and productivity.
Knowledge Transfer and Mentorship
Senior engineers often mentor junior team members. This mentorship process strengthens team cohesion and improves code quality standards. Junior developers benefit from exposure to real world systems, while organizations build internal expertise.
Skill development at early stages supports long term innovation capacity.
Adaptability and Fresh Perspective
Entry level developers often bring recent academic knowledge and exposure to emerging technologies. Their adaptability can contribute to modernization efforts within established teams.
Continuous intake of new talent supports innovation and cultural evolution within development environments.
How Junior Developers Can Stay Competitive in 2026
As hiring expectations evolve, junior developers who focus on strengthening core technical abilities and expanding system awareness improve their career stability. Adaptability and continuous learning remain key factors in long term growth.
Master Programming Fundamentals
Strong understanding of data structures, algorithms, memory management, and debugging techniques forms the foundation of professional development. Developers who understand underlying logic can evaluate and refine automated outputs effectively.
Foundational knowledge increases confidence during interviews and technical assessments.
Develop System Awareness Early
Learning how individual features connect within broader architectures improves value to employers. Junior developers should aim to understand:
-
How APIs communicate
-
How databases interact with applications
-
How services deploy to cloud environments
-
How monitoring and logging systems function
System level awareness differentiates candidates from those limited to surface level coding.
Practice Structured Debugging
Employers value developers who can diagnose issues independently. Practicing root cause analysis, performance profiling, and error tracing builds problem solving strength.
Effective debugging skills often become more important than writing initial code.
Gain Exposure to Cloud and DevOps Tools
Understanding basic deployment pipelines, containerization concepts, and version control collaboration improves employability. Familiarity with modern workflows signals readiness for production environments.
Hands on project experience strengthens credibility.
Build Real Projects
Creating complete projects from design to deployment demonstrates practical capability. Real world examples allow junior developers to showcase problem solving, architectural thinking, and code organization skills.
Portfolio quality often influences hiring decisions more than certifications alone.
Long Term Outlook for Junior Developers
The long term outlook for junior developers depends on structural demand for software rather than short term technological shifts. Software systems continue to expand across industries, increasing the need for trained engineers at all experience levels.
Expanding Digital Infrastructure
Organizations in finance, healthcare, education, logistics, manufacturing, and government services rely heavily on digital platforms. As systems grow more complex, companies require engineers to build, maintain, and improve applications.
Entry level hiring supports this long term expansion by developing future senior talent.
Evolution of Role Responsibilities
Junior developer responsibilities are evolving to include stronger system understanding, debugging proficiency, and familiarity with modern deployment environments. While certain repetitive tasks may require less manual effort, overall technical expectations are increasing.
Role evolution does not equate to role elimination. It reflects higher baseline standards within the profession.
Continued Need for Skill Development Pipelines
Without consistent entry level hiring, organizations risk long term talent shortages. Junior roles remain essential for cultivating future technical leaders, architects, and engineering managers.
Structured mentorship and on the job learning are central to sustaining industry growth.
Adaptation Rather Than Replacement
Technology has historically reshaped developer workflows. Advancements such as high level programming languages, integrated development environments, automated testing tools, and cloud platforms improved efficiency without removing the need for engineers.
Similarly, AI integration appears to be redefining workflows rather than eliminating foundational roles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are junior developer jobs disappearing because of AI
Junior developer jobs are not disappearing entirely. Hiring patterns may fluctuate due to economic cycles and increased competition, but entry level roles remain necessary for long term workforce development. AI tools are changing task execution methods rather than eliminating positions.
Should I start learning programming in 2026
Programming continues to be a foundational skill across many industries. Software development remains central to digital infrastructure, cloud services, cybersecurity systems, and enterprise applications. Learning strong fundamentals and modern workflows supports long term career opportunities.
Will AI reduce entry level developer salaries
Entry level salaries are influenced by regional demand, competition levels, and specialization. While some markets may experience slower salary growth during hiring adjustments, compensation trends are not driven by automation alone.
Is a computer science degree still valuable
A computer science degree provides structured knowledge in algorithms, data structures, operating systems, and system design principles. While alternative learning paths exist, strong theoretical foundations can improve long term adaptability and technical depth.